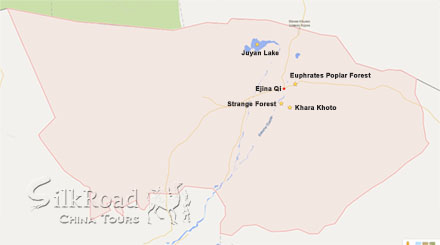
The Euphrates Poplar forest in EjinaQi is one of the three remaining Populus euphratica forest reserves in the world.Dalain Hob, the seat of EjinaQi, serves as a good base camp for a tour of the forests that surround the town, the densest of which are along the Ejin River. Eight bridges span the river, and the areas around the Second Bridge, Fourth Bridge, and Eighth Bridge are the best places to photograph the golden forests.
The Euphrates Poplar forest in EjinaQi is one of the three remaining Populus euphratica forest reserves in the world.Dalain Hob, the seat of EjinaQi, serves as a good base camp for a tour of the forests that surround the town, the densest of which are along the Ejin River. Eight bridges span the river, and the areas around the Second Bridge, Fourth Bridge, and Eighth Bridge are the best places to photograph the golden forests.
Populus euphratica, commonly known as the Euphrates Poplar or Desert Poplar, is a species of poplar tree in the willow family. It is a bushy, deciduous tree whose trunk is often twisted and crooked. It usually grows in desert oases. Though it prefers wet climates, it is resistant to drought, cold, salinity, wind and sandstorms.There is a saying to describe its strong vitality: “Live for a thousand years until death; Stand for another thousand years until fallen; Exist for another thousand years until rotten.”
The Euphrates Poplar is a medium-sized deciduous tree that may grow to a height of about 15 m and a girth of 2.5 m where conditions are favourable. The stem is typically bent and forked; old stems have thick, rough, olive-green bark. While the sapwood is white, the heartwood is red, darkening to almost black at the centre. The roots spread widely but not deeply. The leaves are highly variable in shape. The flowers are borne as catkins, those of the male are 25–50 mm long, those of the female 50–70 mm. The fruits are ovoid-lanceolate capsules, 7–12 mm long, containing tiny seeds enveloped in silky hairs.
The species has a very wide range, occurring naturally from North Africa, across the Middle East and Central Asia to western China. It may be found in dry temperate broadleaf and mixed forests and subtropical dry broadleaf forests at altitudes of up to 4000 m above sea level. It is a prominent component of tugay floodplain ecosystems along river valleys in arid and semi-arid regions, mixed with willow, tamarisk and mulberry in dense thickets. It grows well on land that is seasonally flooded and is tolerant of saline and brackish water. Much used as a source of firewood, its forests have largely disappeared or become fragmented over much of its natural range.
The species requires a lot of light for normal development. It is used in agroforestry to provide leaves as fodder for livestock, timber and, potentially, fibre for making paper. It is also used in afforestation programs on saline soils in desert regions, and to create windbreaks and check erosion. The bark is reported to have antihelminthic properties.
Gallery
Attractions in the area
Related Tours
General Information
Alias: No
Loc: 2 km from Ejina Qi
Entrance: 240 RMB
Open Time: All day
Relevant blogs
-
How did the name of Tianshui in Gansu come about?
The name Tianshui is very pleasant to the ear, and it reminds one of that exquisitely beautiful verse, "After getting drunk, one doesn't know if the sky is in
-
The 8th Silk Road Hotel Festival was successfully held i
On December 27th, the "8th Silk Road Hotel Festival" grandly opened at the Yujing International Hotel in Zhangye. This hotel festival gathered industry experts,
-
The Karez Irrigation System in Turpan has been selected
On September 3rd, at the 75th Executive Council Meeting of the International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage held in Sydney, Australia, the 2024 (11th bat
-
What is the connection between "dragons" and "snakes
In traditional Chinese culture, the snake has a dual identity of auspiciousness and danger. Ancient people believed that the snake not only possesses divine cha
-
Endangered Przewalski's Horses Spotted at Dunhuang Yume
<p>In early February, a group of special "visitors"—the Przewalski's horses—appeared at the Dunhuang Yumen Pass scenic area in Gansu Province, a U
-
The Fourth Dunhuang Cultural Tourism Supplier Conference
On the morning of February 18th, the Fourth Dunhuang Cultural Tourism Supplier Conference in Northwest China commenced at the Dunhuang International Convention